Plastic injection molding is now one of the most strategic technologies in modern industry. This molding process, which transforms plastic materials into high-quality finished parts, raises many practical questions for professionals: When should you favor this technique? How can you optimize the quality-to-cost ratio for small production runs? What are the advantages and limitations of different approaches?
This article provides an overview of plastic injection molding — from the benefits of the process to automated industrial solutions, including our manual press, HoliPress, which is ideal for prototyping and small production. We conclude with a detailed comparison to help you choose the production method best suited to your needs.
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing method used to produce parts from thermoplastic materials. The technique involves melting plastic by heat and injecting it under pressure into a closed mold, where it solidifies into the desired shape.
This molding process has become one of the most widespread manufacturing methods thanks to its exceptional ability to produce precise, durable, and repeatable parts. The careful design of molds is at the heart of the process, directly determining the final part quality.
Plastic injection molding stands out for its versatility in material selection. A wide range of plastics can be processed — from standard to high-performance engineering materials — each providing specific properties according to the application. This variety allows production to meet mechanical, thermal, or aesthetic requirements.
The efficiency of the process lies in its optimized quality-to-cost ratio. While the initial investment is significant, especially for precision mold fabrication, the cost is amortized during large-scale production. Injection molding therefore combines technical excellence with economic profitability, explaining its widespread use in industries such as automotive, electronics, and packaging.

High repeatability
Injection molding produces consistent series parts, with accuracy depending on process parameters.

Compatibility with many polymers
Soft thermoplastics (TPE), rigid (ABS, PP), engineering (PA, POM), recycled or bio-based — the process adapts to many formulations.

Fine details and professional finishes
Precise molds enable complex geometries, surface textures (matte, glossy, grained), and even integrated markings.

Excellent productivity
Once the mold is ready, each injection cycle lasts only seconds to minutes, enabling rapid serial production.

Strong, functional parts
Molded parts are durable and usable without major post-processing — suitable for both prototyping and final production.
This process includes several key steps:


The mold is the true core of the process. It defines not only dimensions but also complex geometries, surface finishes (smooth, textured, grained), and sometimes even functional features such as inserts or parting lines. It usually consists of two main halves (cavity and core) and must be precisely machined to ensure repeatability and sealing during injection.
An upcoming white paper (stay informed via our newsletter) will detail the design of 3D-printed molds compatible with our HoliPress machines. Resin 3D printing is revolutionizing mold fabrication by drastically reducing lead times and complexity. This innovative approach allows injection-molded parts to be produced within just a few days, transforming traditional development cycles. We will also discuss machined molds, which offer key benefits — foremost being their strength.
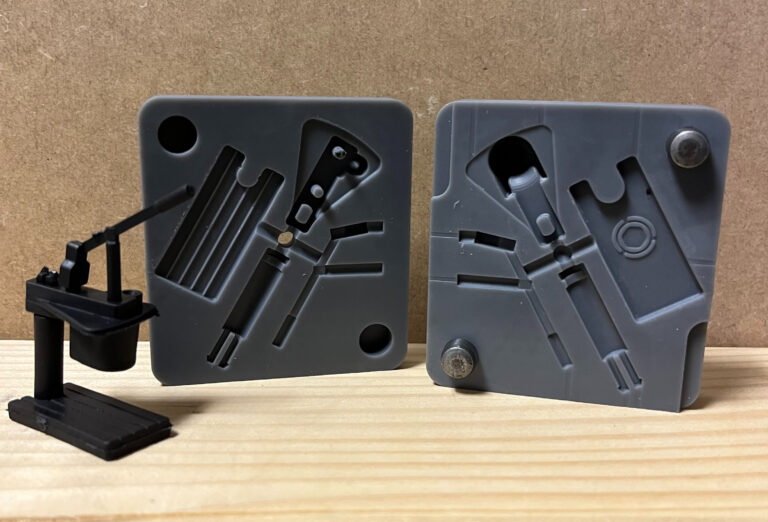

The polymers used are thermoplastics, which can melt when heated and solidify again without significant loss of mechanical properties, allowing for reuse or recycling. Various families of plastics are commonly used:
Engineering (PA, POM, PC) for high mechanical performance,
Standard (PP, PE, PS) for everyday objects,
Flexible (TPE, TPU) for soft applications,
Recycled or bio-based plastics depending on requirements.
Feel free to contact us to explore our material collection or to perform tests before purchasing a machine. If you would like us to test your own material, you can contact us here.
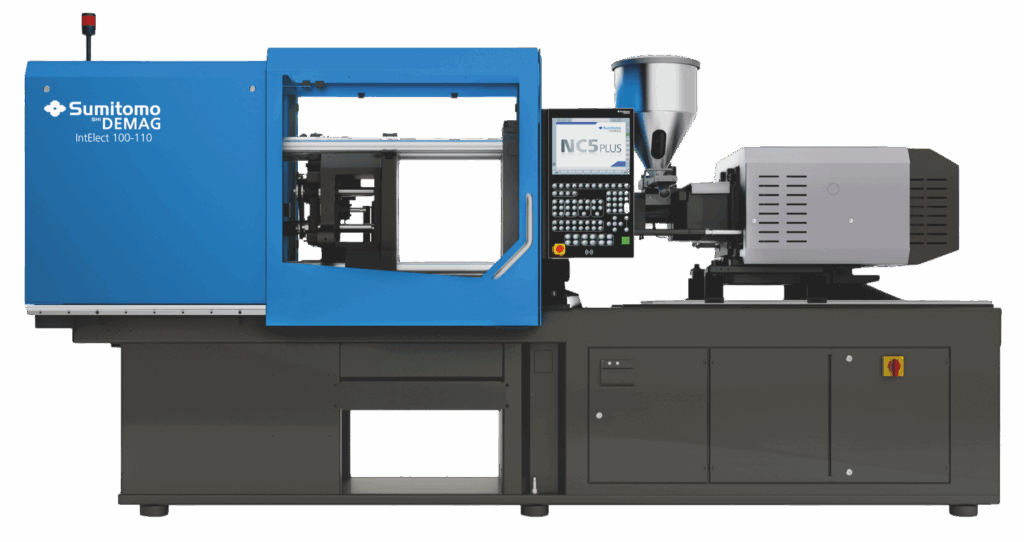
Principle: a fully (sometimes partially) automated injection press performs thousands of continuous cycles.
Advantages: very high precision, speed, high throughput, precise process control.
Applications: mass production, technical components, electronic parts, automotive parts.
Drawbacks:
Manual plastic injection is an affordable and flexible alternative to industrial injection for prototyping and small production. It allows designers, engineers, educators, R&D teams, and start-ups to produce genuine injection-molded parts without the need for an industrial workshop or heavy investment.
The HoliPress is a compact, manually operated injection press designed and manufactured in France. Developed for rapid prototyping, micro-series production, lab testing, and education, it makes plastic injection straightforward — suitable for schools, design offices, and small manufacturers alike.
How it works: plastic pellets (virgin or recycled) are poured into a vertical heating chamber. Using precise temperature control via a dedicated unit, the material is melted and then manually injected into a mold with a mechanical lever. This direct injection offers good repeatability and controlled dosing. Compatible molds include resin (3D printed) or machined (aluminum, steel, etc.) types.
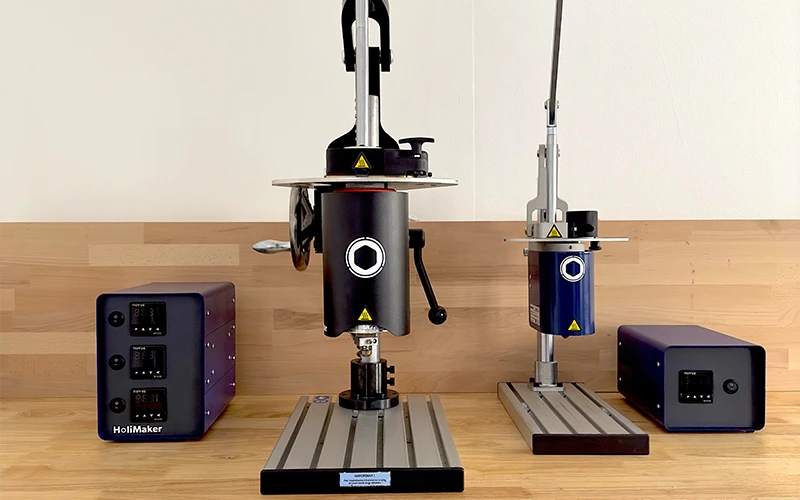

Key benefits:
Affordable: HoliPress costs 10 to 100 times less than an industrial press, ideal before moving to high-volume production.
Easy installation: compact and lightweight, works with a standard outlet and mounts easily to any sturdy workbench.
Versatile: suited for small productions, design iterations, and material testing — including recycled plastics.
User-friendly: visible mechanics, intuitive interface, and straightforward operation make it ideal for learning and demonstrations.
Material compatibility: processes most thermoplastics (TPE, PA, PP, ABS, PS, POM, etc.).
Flexible mold options: works with SLA resin 3D-printed molds or machined molds for more technical parts.
Simple maintenance: reliable, streamlined design with easily replaceable wear parts.
In summary, the choice between industrial injection moulding and manual injection moulding depends on the volume, budget and flexibility required. HoliPress offers a simple and economical solution for prototyping or small-scale production, while industrial injection moulding remains the benchmark for high-speed and mass production.

Criterion | Automated Industrial Press | HoliPress |
Initial investment | €25,000+ - €200,000+ | From €3,000 |
Mold cost | €5,000+ - €150,000+ | €300 - €3,000 |
Time to first part | Several weeks/months | Hours/days |
Production volume | High-volume series | Prototyping and small series |
Part complexity | Very high | High |
Flexibility/iterations | Low (fixed mold) | Very high |
Maintenance/accessibility | Requires expertise | Simple, autonomous |
Please contact us if you would like more information about HoliPress.
Plastic injection molding is a powerful process but often difficult to access outside heavy industrial settings. Yet many stakeholders — start-ups, design offices, R&D labs, innovation departments — need its benefits for low-volume runs, functional prototyping, or technical training. With agile solutions like HoliPress, it becomes possible to test ideas quickly, iterate freely, and prepare for industrial production while controlling costs and lead times.
Share it
À propos
HoliMaker est une entreprise innovante qui conçoit, produit et commercialise des outils de micro-industrie destinés à la transformation du plastique. HoliMaker propose également des ateliers et des formations à la manipulation de la matière.
HoliMaker est une startup de la Région Grand Est implantée dans le Sillon Lorrain.
Implantés à Metz en Moselle, HoliMaker préserve un savoir-faire local à travers son écosystème de fournisseurs Français, de fabricants de matériaux, de sous-traitants mais aussi de partenaires revendeurs.
Nous repoussons les standards de qualité et de savoir-faire. Toutes les pièces sont assemblées dans nos locaux
HoliMaker is an innovative company that designs, produces and markets micro-industrial tools for plastic processing. HoliMaker also offers workshops and training courses in material handling.
HoliMaker is a startup from the Grand Est region, based in the Lorraine region.
Based in Metz, Moselle, HoliMaker preserves local know-how through its ecosystem of French suppliers, material manufacturers, subcontractors and reseller partners.
We push back the standards of quality and know-how. All parts are assembled on our premises.